Part of an electromagnet is called a solenoid.
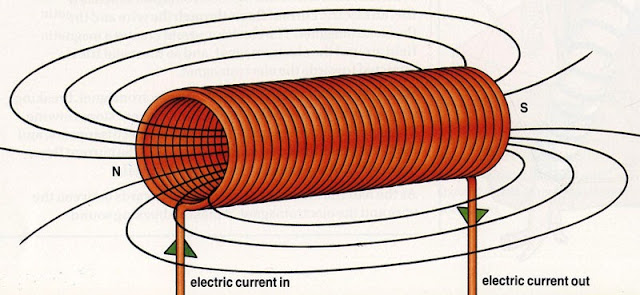
A solenoid is a coil of wire that has an electric current flowing through it. When an electric current flows through a wire, the electricity creates a magnetic field around the wire.
If the wire is wound into a coil, the magnetic field around the coil becomes much stronger.
We can make the magnetic field even stronger by putting a rod of iron or steel into the solenoid.
The magnetic field becomes stronger because the metal rod is magnetized by the solenoid.
Like a bar magnet, a solenoid has two poles.
The flux lines of the magnetic field link together the north and south poles of the solenoid.
When an iron rod comes into a magnetic field around a solenoid, the domains in the rod all line up and point one way.
Then the rod has strong magnetic poles at each end and a magnetic field around it.
When an electric current runs through a solenoid, it has poles just like a bar magnet.
One end is a north pole and the other end is a south pole.
If you hold an iron or steel rod near a solenoid, the rod becomes magnetized, and the end of the rod that's nearest the north pole of the solenoid becomes a south pole.
In the same way, the end of a rod held near the south pole of the solenoid will become a north pole.
Unlike poles attract, and so the magnetized rod and the solenoid attract each other.
A solenoid is a coil of wire that has an electric current flowing through it. When an electric current flows through a wire, the electricity creates a magnetic field around the wire.
If the wire is wound into a coil, the magnetic field around the coil becomes much stronger.
We can make the magnetic field even stronger by putting a rod of iron or steel into the solenoid.
The magnetic field becomes stronger because the metal rod is magnetized by the solenoid.
Like a bar magnet, a solenoid has two poles.
The flux lines of the magnetic field link together the north and south poles of the solenoid.
How does a solenoid magnetize an iron rod?
The iron rod is made up of lots of groups of atoms called domains. These domains are miniature magnets, but their magnetism has no power because their poles are pointing in different directions.When an iron rod comes into a magnetic field around a solenoid, the domains in the rod all line up and point one way.
Then the rod has strong magnetic poles at each end and a magnetic field around it.
When an electric current runs through a solenoid, it has poles just like a bar magnet.
One end is a north pole and the other end is a south pole.
If you hold an iron or steel rod near a solenoid, the rod becomes magnetized, and the end of the rod that's nearest the north pole of the solenoid becomes a south pole.
In the same way, the end of a rod held near the south pole of the solenoid will become a north pole.
Unlike poles attract, and so the magnetized rod and the solenoid attract each other.
Electromagnet experiment for kids - What can Solenoids do?
You can make a solenoid and see for yourself how a steel rod moves inside the coil when the electric current flows.
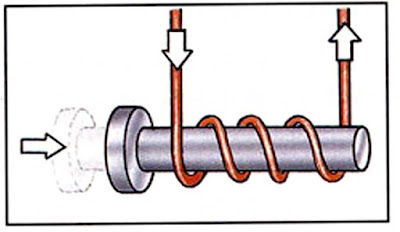
1. Cut a piece of the drinking straw about 1 inch {2.5 centimeters) long.
Wind the wire many times around the short piece of straw to make a solenoid.
Always wind the wire in the same direction.
Leave about 10 inches (25 centimeters) of wire free at each end.
2. Connect one end of the solenoid wire to one terminal of the battery.
3. Stand the pin upright on the table. With the other hand, place the solenoid over the pin. Hold the solenoid upright with the pin inside it.
4. Hold the free wire from the solenoid against the free battery terminal and the electric current will flow.
Don't touch the bare end of the wire!
As the current flows, the pin jumps up into the coil.
It will stay there until the current is switched off.
5. Now switch the connections to the battery.
Does the pin still jump up into the solenoid?
Does it matter in which direction the electric current flows through the coil?
Solenoids at work
Solenoids can pull iron rods towards them.
Can you think of ways in which a solenoid can be useful?
Solenoids can work as a kind of switch in electric door locks, in pinball machines, and in electric circuit breakers.
Can you think of ways in which a solenoid can be useful?
Solenoids can work as a kind of switch in electric door locks, in pinball machines, and in electric circuit breakers.
When you press down a switch on an electric door lock, an electric current flows through a solenoid and creates a magnetic field around it. When the current flows, the metal rod in the lock becomes magnetized and is pulled into the coil. This action pulls the bolt back and the door is unlocked.
Solenoids and magnets
If we use a solenoid with a magnet, instead of an ordinary iron rod, the solenoid can not only pull the magnet towards the coil, but also push it away.
So the magnet moves both backwards and forwards.
So the magnet moves both backwards and forwards.
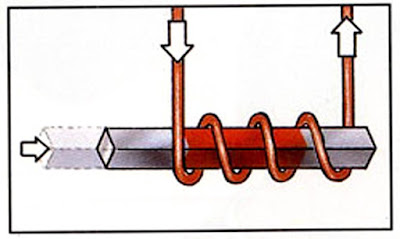
1. When an electric current flows through the coil, the rod becomes magnetized. It is pulled inside the coil.
2. The electric current is now reversed and it flows in the opposite direction. The rod is again magnetized and pulled inside the coil.
3. The rod is now replaced by a bar magnet.
When an electric current flows through the coil, the bar magnet is pulled inside the coil.
4. What happens when the electric current is reversed? The coil pushes the magnet away. When the current flows in a different direction, the magnet moves in a different direction.
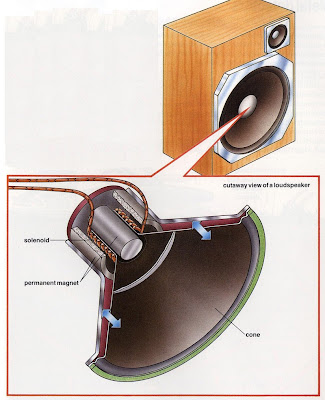
Inside a loudspeaker
Loudspeakers can turn electric signals into sounds that we can hear. Inside a loudspeaker there is a solenoid attached to a thin cone. The solenoid is also attached to a powerful permanent magnet. Wires connect the solenoid to a sound system or a television. Electric signals pass through these wires and through the solenoid. The signals are vibrations carried by an electric current.
The solenoid moves backwards and forwards as the electric signals vibrate at different speeds, up to 40,000 times a second. This makes the cone vibrate. The vibration of the cone makes the sounds we hear.















Social Plugin